Extrusion lamination and co-extrusion lamination (extrusion coating)
Definition of extrusion lamination and extrusion coating lamination (co-extrusion)
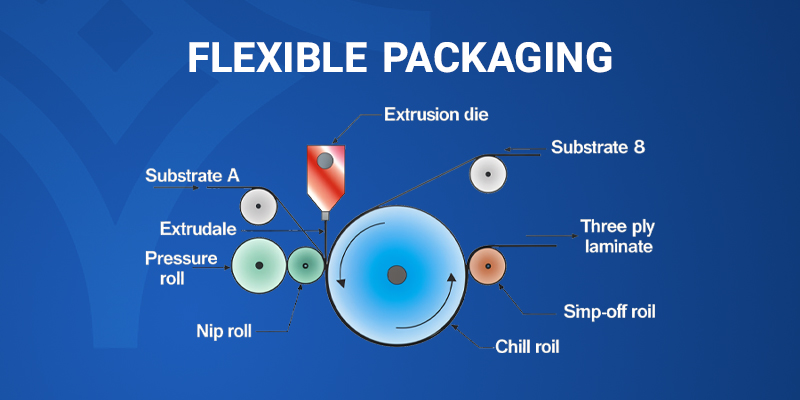
What is extrusion lamination?
Extrusion lamination is a process in which a material undergoes plastic deformation by applying force. This material takes on the cross-sectional shape of the mold, and if the material has suitable properties, that shape remains in the final extrudate. Extrusion lamination is a laminating technique that involves extruding thermoplastic materials such as PE or PP films.
This process begins with feeding thermoplastic materials into an extrusion machine, where they are melted and transformed into a flat sheet using a flat die. The sheet film is then directed to the laminating section, where one or two films are laminated onto it using cooling rollers and laminating rollers.
Types of lamination methods in flexible packaging
What is co-extrusion lamination or extrusion coating?
Co-extrusion involves bonding two or more layers together using a molten polymer.
In this process, a molten polymer film is extruded between two substrates, usually flexible layers. This thin layer is coated onto another substrate and immediately passes through cooled rollers to form a strong bond, winding up in the form of a reel. Extrusion lamination is commonly used in flexible packaging applications such as snack food bags, stand-up pouches, and multi-layer films.
Classification of the extrusion lamination process
Laminated films can be produced through two main processes: Extrusion laminate and Coextrusion laminate (Extrusion Coating).
Extrusion lamination
Extrusion lamination involves the simultaneous extrusion of two or more layers of molten polymer. The layers are then combined and bonded to substrate materials, usually a film or paper, using pressure and/or heat. This process results in a laminated multi-layer film where each layer has different characteristics such as barrier properties, strength, printability, or heat resistance. Extrusion lamination is similar to extrusion coating, where resin is extruded between two substrates and acts as a bonding agent.
Extrusion lamination offers several advantages. First, it has lower costs and requires less investment, making it an economical option. Additionally, the production facility remains clean as there is no need for solvent-based adhesives, eliminating the issue of residual solvents in the laminated film.
Extrusion lamination also has high production efficiency. This process is straightforward and allows for rapid production, thus increasing output. Furthermore, the user-friendly control system makes it easier for operators to manage and control the lamination process.
Overall, extrusion lamination plays an important role in the plastic lamination process. Its cost-effectiveness, clean production, absence of residual solvents, high production efficiency, and user-friendly control make It a valuable technique in the plastic lamination industry.
Common problems in the lamination process.
Typical structure of extrusion lamination
- Vacuum Bag: NY//PE/PE
- Gel Coating Film: PET/MPET//PE//EVA, PET/PET//PE//EVA, NY/EVOH//EVA, NY/PE//EVA
- Packaging for Puffed and Lightweight Foods: BOPP//PE/MCPP, BOPP//PE/MPET/PX(CPP), BOPP//PP, BOPP//PE, BOPP//PE/CPP
- Sauce: PET//PE/AL//SURLYN, PET/AL//PE/PE, PET/NY/AL//EAA/PE
Extrusion coating and lamination lines are typically custom-built and can be used for various applications:
- Liquid packaging
- Aseptic beverage containers
- Flexible packaging
- Toothpaste tubes
- Medical packaging
- Bags for products like cement, grains, and dry chemicals
Co-extrusion or extrusion coating
Co-extrusion involves applying a molten polymer onto a substrate, usually a film or paper, using an extrusion die. The polymer is extruded and then immediately attached to the substrate, forming a multi-layer structure. This process creates a single-layer laminated film where the polymer coating provides protection, barrier properties, or aesthetics for the substrate. Multi-layer extrusion combines various properties of multi-layer polymer structures that affect the strength and toughness of the materials. The polymer structures produced by co-extrusion depend on processability and barrier requirements.
In the extrusion coating process, extruder forces push thermoplastic resin through a horizontal gap onto a moving web of substrate. The resulting product is a film structure with a permanent coating.
In the field of laminated coating packaging, the backing is typically made from materials such as printed PET, BOPP, paper, and others. An example of a typical laminated coating packaging structure is an instant noodle bag, which usually consists of a printed BOPP layer with LDPE (or PP).
In the lamination process, the first backing layer typically includes materials such as PET, BOPP, PA (nylon), and paper, among others. The second substrate can be made from LDPE (low-density polyethylene), CPP (cast polypropylene), aluminum foil, or metal film. The extrusion resin used in this process is usually PE (polyethylene), PP (polypropylene), EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate), or EAA (ethylene-acrylic acid).
This method can be applied to packaging for common laundry detergents, resulting in a structure composed of printed BOPP, extrusion resin, and polyethylene film.
Co-extruded laminates provide a composite substrate that is very difficult to separate. The composite substrate inherits greatly improved physical properties and barrier performance from its constituent elements.
Summary
Both co-extrusion and extrusion lamination methods are widely used in the production of laminated films. These processes offer advantages such as efficient production, customization of film properties, and the ability to create multi-layer structures suitable for various packaging applications.
In summary, co-extrusion and extrusion lamination are two techniques used to produce laminated films. Each process offers unique benefits and allows for the creation of films with specific characteristics to meet different packaging needs.
Co-extrusion and extrusion lamination are conversion processes that allow different backing materials to combine to achieve a single composite structure. The materials involved may include plastics, paper, cardboard, or aluminum foils.
Many flexible packaging applications require multiple layers of film and a combination of features to meet consumer demands. To achieve packaging characteristics such as rigidity, aesthetics, and barrier properties, several different films can be laminated together in the extrusion layering process, which joins two or more layers of film In an extensive network format using an extruded polymer as an adhesive.
If the substrate does not adhere well to the extrudate, if the backing and extrudate do not have sufficient barrier properties, or if the line speed is too fast, the final structure may be compromised. Adding primers to the extrusion lamination process can significantly improve adhesion and other properties without reducing the speed of the process.
