
Application of polyurethane in construction
The nature of polyurethanes allows them to adapt to solve challenging problems, mold into unusual shapes, and enhance industrial and consumer products. The chemistry of polyurethane can be essential for ongoing advancements in environmental care and the efficient use of our natural resources.
Polyurethane is a highly versatile material capable of addressing many issues and is used in construction, furniture, bedding, automotive, bookbinding, and many other industries. Because polyurethanes are durable, lightweight, and versatile, they can help reduce waste and lower energy consumption. Energy efficiency and recycling remain significant issues that both industry and consumers face.
Polyurethane laminate adhesive
Polyurethanes are found in all aspects of building construction, from product manufacturing to meeting essential practical needs on site. They are used as insulation, adhesives, sealants, and glues in various building products and numerous other applications. The desire and need for more energy-efficient buildings have encouraged increased use of polyurethane products.
Along with the rest of the plastics industry, the polyurethane industry supports methods to conserve resources and minimize the environmental and health impacts of plastics and plastic products.
Everything starts with the chemistry of the two raw materials used to manufacture polyurethane products – methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI). A major reaction of MDI and TDI in the environment is the formation of neutral solid polyureas from reaction with water.
MDI
Approximately 5 million tons of methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) are produced and used globally each year for the production of polyurethanes. This substance is well-controlled, with only small amounts – from milligrams to a few grams per ton of MDI used – being released into the environment. A major reaction of MDI in the environment is the formation of neutral solid polyureas from reaction with water. When used, MDI reacts with polyols to form various polyurethane products. Polyurethanes have been shown to be stable in the environment and during disposal, with no adverse effects on municipal waste management processes, landfilling, or incineration.
TDI
Approximately 2 million tons of toluene diisocyanate (TDI) are produced and used globally each year for the production of polyurethanes. This substance is also well-controlled, with only small amounts – a few grams per ton of TDI used – being released into the environment. One of the main reactions of TDI in the environment is the formation of neutral solid polyureas from reaction with water. In use, TDI reacts with polyols to form various polyurethane products. Like MDI, polyurethanes have been shown to be stable in the environment and during disposal, with no adverse effects on municipal waste management processes, landfilling, or incineration.
solventless laminating adhesive
Application of polyurethane in building and construction
Modern homes require high-performance materials that are strong yet lightweight. They perform well but are easy to install. They are durable but also versatile. Polyurethane helps conserve natural resources and contributes to environmental preservation by reducing energy consumption. With an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, insulation properties, durability, and adaptability, polyurethane is often used in building and construction applications. Both the cost-effectiveness of these versatile materials and the convenience they provide for homeowners have made polyurethane components a part of homes everywhere.
Polyurethane is used throughout the home. In flooring, flexible foam underlays cushion your carpet. On roofs, reflective plastic coatings on polyurethane foam can reflect sunlight and heat, helping keep homes cool while also reducing energy consumption. Polyurethane building materials offer design flexibility for new homes and renovation projects. Core foam panels provide a wide range of colors and profiles for walls and ceilings, while foam entry doors and garage doors are available in various colors and styles.
Heating and cooling account for about 56% of energy consumption in a typical home, making it the largest energy expense for most households. To maintain consistent temperatures and reduce noise levels in homes and commercial properties, builders turn to rigid polyurethane and polyisocyanurate foam. These foams are effective insulating materials that can be used in roof and wall insulation, insulated windows, doors, and air barrier sealants.
-
Composite wood
Polyurethanes play a significant role in modern materials such as composite wood. Polyurethane-based binders are used in composite wood products to permanently bond organic materials to oriented strand boards, medium-density fiberboards, long strand lumber, multilayered plywood, and even straw board and particle board.

-
Flooring
Whether as a foam underlayment or as a coating on top, polyurethanes can make the floors we walk on every day more durable, easier to maintain, and aesthetically pleasing. The use of flexible polyurethane foam as carpet padding in residential or commercial applications can significantly extend the lifespan of carpets, protect their appearance, provide greater comfort and support, and reduce ambient noise.

Polyurethanes are also used for flooring coverings, from wood and parquet to concrete. This protective coating is resistant to wear and solvents and is easy to clean and maintain. With a polyurethane coating, a new wooden, parquet, or concrete floor lasts better and longer, while an old floor can be restored to look new again.
-
Polyurethane coatings
Other types of polyurethane coatings are used in construction, where building floors, steel trusses, and concrete supports are sprayed to enhance durability and reduce maintenance costs. For example, this coating makes cleaning suspended bridges easier, helps prevent rust on their supporting beams, and improves their appearance even from a distance.
Products made from polyurethane support important environmental goals. For instance, rigid and spray polyurethane foams used for thermal insulation can significantly increase the energy efficiency of residential and commercial buildings. In addition to energy savings in heating and cooling buildings, polyurethanes can contribute to the greater durability of structures and reduce the burden on raw material resources for their maintenance or upgrades. Polyurethanes are also used as wood adhesives to produce highly functional boards and strong structures from waste wood that would otherwise be disposed of.

At the end of their useful life, polyurethanes can be sent for reuse (e.g., re-bonding), chemically recycled, or incinerated for energy recovery based on national, regional, and local regulations. Today, there are more options for reusing polyurethanes.
-
Structural insulated panels (SIPs)
SIPs are engineered panels made of a thick layer of polyurethane or polyisocyanurate foam sandwiched between two layers of oriented strand board, plywood, or cement fiberboard. SIPs are used throughout the building: In framing, flooring, roofing, and as a single-piece exterior covering.
Benefits
As the name suggests, SIPs provide both structural support and incredible insulating properties with multiple advantages:
- Simplicity and elegance in single-piece design
- Ability to withstand severe winds and seismic forces
- Efficient thermal performance that can reduce energy consumption
- A dense and continuous air barrier for effective insulation properties with high R-value
- Customizable sizes for increased design flexibility
- Easy control of lightweight smaller panels that can be installed by one person
- Ease of assembly on-site, leading to shorter construction timelines
- Additional structural strength across the entire panel span
-
Pipe insulation
Rigid polyurethane foam is increasingly used for insulating and protecting pipes and pipelines. Today, polyurethane foam is used for oil and gas pipelines, heating pipes, power plant piping, chemical facility piping, and even swimming pool pipelines.

Benefits
The widespread use of rigid polyurethane foam in pipe and pipeline insulation is based on many advantages. It can:
- Help reduce heat loss for energy savings.
- Be resistant to extreme cold and heat.
- Assist in controlling the surface temperature of pipelines to protect workers.
- Help maintain appropriate temperature control for sensitive manufacturing processes.
- Prevent condensation on cold surfaces.
Reduction or prevention of equipment damage caused by firefighting systems
It creates a sound barrier for noise control.
It possesses exceptional mechanical strength.
-
Spray polyurethane foam (SPF)
Spray polyurethane foam is produced from a mixture of rapidly reacting foam components that are combined in a special mixing spray gun at the moment of use. The foam density can be adjusted for specific applications and can be applied to almost any substrate that is clean, dry, and free of debris or dust. This reaction quickly results in a fully risen and non-sticky surface, and it also acts as a sealant. The foam may be protected with another coating such as fire retardant or weather barrier. SPF is used for insulating walls and ceilings in commercial, industrial, agricultural, and residential environments, as well as for insulating industrial pipes, cold storage facilities, and marine floating devices.

Benefits
The distinctive SPF technology offers unique advantages:
- High R-values—up to 7 per inch—result in reduced energy costs.
- Closed-cell spray polyurethane foam acts as both an air barrier and a Class II vapor retarder.
- Spray polyurethane foam delays air transfer and minimizes the infiltration of air and sound, pollutants, and pollen that often penetrate buildings.
- It can be applied to challenging or architecturally complex structural features such as cathedral ceilings, thereby enhancing design creativity.
- Some SPFs help control moisture and condensation, reducing mold growth.
- Some SPFs add structural strength and can actually help buildings withstand high winds and storms.
Polyiso board stock
Polyiso is commonly used in the construction of hospitals, warehouses, retail stores, schools, manufacturing facilities, and residential homes. On a per-inch basis, polyiso is one of the most energy-efficient insulation products available on the market. Due to its high R-value and thin profile, polyiso allows builders to use less insulation while creating thinner walls and roofs.
Benefits
Polyiso offers unique advantages:
- Polyiso has an R-value per inch of thickness.
- Polyiso repels water and is moisture-resistant.
- Polyiso is resistant to solvents such as construction adhesives.
- Polyiso insulates buildings across a wide range of temperatures.
- Polyiso is readily available nationwide.
PU insulation coating
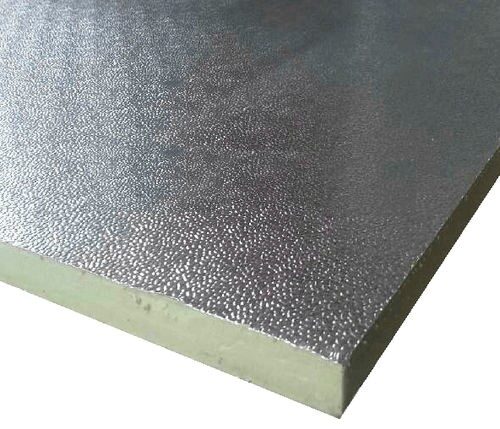

The insulation coating, which typically consists of polyiso foam placed between reinforced aluminum foil, can significantly reduce energy loss in buildings, particularly in walls. Common wooden or steel studs in walls and ceilings create a “thermal bridge” that allows warm or cold air to pass into the building. The insulation coating works to reduce energy loss. In fact, many building codes now require continuous insulation on the exterior of buildings. Insulation foam coatings are widely used for walls and some roofing applications in new commercial, residential, agricultural, and industrial buildings, as well as during the renovation of existing buildings to improve thermal performance.
Benefits of using polyurethane in construction
1. Sustainability
Environmental criteria and energy efficiency are key factors in product design and purchasing decisions, along with product safety, cost, performance, and availability.
Environmental and energy performance criteria are evaluated through a “system” approach using recognized life cycle analysis tools that encompass the entire “use” phase.
Sustainable product criteria reflect consensus-based decision-making, best available science, transparency, and openness to all stakeholders.
2. Energy efficiency
Energy savings in buildings are becoming increasingly important every day. A significant percentage of our nation’s energy is used for heating, cooling, and powering our homes and buildings. Energy lost through walls, roofs, and windows represents the largest energy waste in most buildings. Energy loss in buildings translates to additional operational costs, loss of comfort, and reduced productivity. When it comes to energy efficiency in buildings, plastic-based products such as rigid polyurethane foam (PUR), spray polyurethane foam, and polyisocyanurate foam insulation (PIR or polyiso) are at the forefront of discussion as they are among the most efficient options available.

Thermal insulation products for buildings work to reduce heating and cooling losses and improve the efficiency of building envelopes. The performance of insulation is typically measured by Its R-value, or thermal resistance. The higher the R-value, the better the material insulates against heat transfer. PUR (polyurethane) and PIR (polyisocyanurate) foams have the highest R-values per inch among all commercial insulation products available. With typical R-values ranging from R 3.6 to R 7.2 per Inch, polyurethane products allow for energy-efficient designs with thinner walls and low-profile roofs. This enables architects or engineers to maximize usable space in a building while simultaneously reducing operational costs.
Innovative material design and technological advancements have led to the production of high-quality polyurethane insulation products that reduce energy waste. Greater energy efficiency impacts operating costs. Highly efficient walls and roofs may allow heating and cooling equipment to be reduced by up to 35%. This can translate to more usable floor space at the same overall cost.
3. Lower costs
When a building’s air is heated or cooled, polyurethane insulation and polyiso foam help keep it inside the building, contributing to lower energy bills. Polyurethane and polyiso foams can help building owners save on energy bills from day one of installation. Polyurethane insulation systems create air barriers in attics, walls, and under floors, effectively separating the building from the elements to aid in energy savings. Additionally, buildings insulated with polyurethane foam often require smaller heating and cooling units, which can save the building owner additional costs.
4. Keeping outside air out
Air typically finds its way into homes through holes and gaps in attics, floors, foundations, or exterior walls, reducing the energy efficiency of the building while also bringing in dust, pollutants, noise, and moisture. Air barriers control this infiltration by creating a seal around the building’s ventilation system and the entire building envelope.
Polyurethane and polyiso insulation systems create a tight barrier around your home that helps prevent outside air from infiltrating and inside air from escaping.
5. Versatility
A range of polyurethane products—both for interior and exterior use—enables significant diversity in design and performance. The thin profile of many polyurethane products allows architects greater flexibility in creative design while maximizing interior space.
Some polyurethane foam insulations can conform to any size or shape instead of being placed between traditional uniformly spaced studs or beams.
Bay windows, angled walls, curved or arched roofs—virtually any unconventional framing design can be well insulated and secured with polyurethane insulation, creating greater flexibility in design, energy efficiency, and usable space.
6.Comfort
Polyurethane insulation creates a tight barrier around buildings due to its ability to prevent air movement, helping to keep out pollen, dust, allergens, and other irritating and unhealthy pollutants. Polyurethane and polyiso insulation also help prevent moisture and condensation throughout the building envelope, delaying mold and mildew growth.
Noisy neighbors or busy streets? Polyurethane foam insulation has another advantage: It helps block neighborhood noise for a quieter, more comfortable building.
Energy-efficient buildings, such as those using polyurethane and polyiso foam products, consume less energy for heating and cooling, require less fossil fuel consumption, and emit fewer greenhouse gases.
7. High performance
Traditional fiber insulation products must be supported or protected by surrounding materials due to their low density. These insulation materials can be soft or sensitive to moisture, which is not the case with polyurethane insulation products. Polyurethane foam is a thermal insulation that provides structural performance and fire resistance. Polyurethane products are strong yet lightweight, dimensionally stable, moisture-resistant, and durable.
This combination of properties allows manufacturers to design polyurethane thermal insulation products for various applications and enables them to bond to a wide range of substrates. Additionally, when combined with the appropriate materials, they can act as barriers to external air, helping to prevent outside air infiltration and inside air escape.
