
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
What is thermoplastic polyurethane?
Thermoplastic polyurethane, or TPU for short, is a linear block copolymer made up of hard and soft segments.
Soft segment (polyether or polyester): This segment is made from polyols and isocyanates, providing flexibility and the elastomeric properties of TPU.
Hard segment (aromatic or aliphatic): This segment consists of a chain extender and isocyanate, which gives TPU its toughness and physical performance characteristics.
- Aromatic TPUs are based on isocyanates like MDI.
- Aliphatic TPUs are based on isocyanates like H12 MDI, HDI, and IPDI.
When these isocyanates are combined with diols with small chains, they produce hard blocks. Typically, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is aromatic; however, when color retention and clarity against sunlight are priorities, they can also be aliphatic.
Thermoplastic polyurethanes are elastic and melt-processable. Additives can improve dimensional stability and heat resistance, reduce friction, and enhance flame resistance, fungal resistance, and weatherability.
Aromatic thermoplastic polyurethanes are strong, versatile resins that resist microbial attack and perform well against chemicals. However, an aesthetic drawback is the tendency of aromatics to degrade via free radical pathways due to exposure to heat or ultraviolet light. This degradation results in color change and loss of physical properties.
Additives such as antioxidants, UV absorbers, and amine stabilizers are used to protect polyurethanes from oxidation caused by ultraviolet radiation, making thermoplastic polyurethanes suitable for a wide range of applications that may require thermal and/or optical stability.
On the other hand, aliphatic thermoplastic polyurethanes are inherently light-stable and resistant to color change due to UV exposure. They are also optically clear, making them suitable laminates for encapsulating glass and security windows.

Currently available thermoplastic polyurethanes can be primarily divided into two groups based on the chemistry of the soft segment:
- Polyester-based TPUs (mainly derived from adipic acid esters)
- Polyether-based TPUs (mainly based on tetrahydrofuran (THF) ethers).
Main types of thermoplastic polyurethane films:
The main chemical classes of TPU films are polyester, polyether, and polycaprolactone.

1. Polyester thermoplastic polyurethane
• Polyester TPUs are resistant to chemicals and oils and are abrasion-resistant.
2. Polyether thermoplastic polyurethane
• Polyether TPUs have a lower specific gravity compared to the other two and exhibit better abrasion and tear resistance. They are resistant to hydrolysis and microbial attacks and have flexibility at low
temperatures, making them an excellent choice for pipelines that require these properties.
3. Polycaprolactone thermoplastic polyurethane
• Polycaprolactone TPUs are hard, durable, have low-temperature performance, and high resistance to hydrolysis, making them a preferred raw material for manufacturing pneumatic and hydraulic seals.
Polycarbonate diols (PCD)
Another interesting category of polyols used for producing thermoplastic polyurethane includes polycarbonate diols, which are generally used to create polyurethanes that combine carbonate linkages for superior performance. Polycarbonate-polyurethanes can also be produced using polyurethane prepolymers based on polycarbonate.
A polyurethane prepolymer based on polycarbonate is derived from the corresponding polycarbonate diol in which all hydroxyl (OH) end groups of the polyol have reacted with an isocyanate, leaving isocyanate (NCO) groups at the ends instead of hydroxyls.
Compared to polycaprolactone and PTMEG-based polyurethanes, PU elastomers based on PC-PU prepolymers exhibit:
- Exceptional durability
- Higher chemical resistance
- Improvement of hydrolytic stability
- Increased thermal resistance
- Better abrasion resistance
- Superior mechanical properties
Thermoplastic polyurethane offers a wide range of physical and chemical properties for the most demanding applications, such as automotive, wire and cable, breathable films for leisure, sports coatings, textile coatings, non-yellowing and non-yellowing films, etc.
These properties lie between those of plastics and rubber. Thanks to its thermoplastic nature, TPU has various advantages over other elastomers that cannot match it, such as:
- Excellent tensile strength
- Increased elongation at break
- Good load-bearing capacity
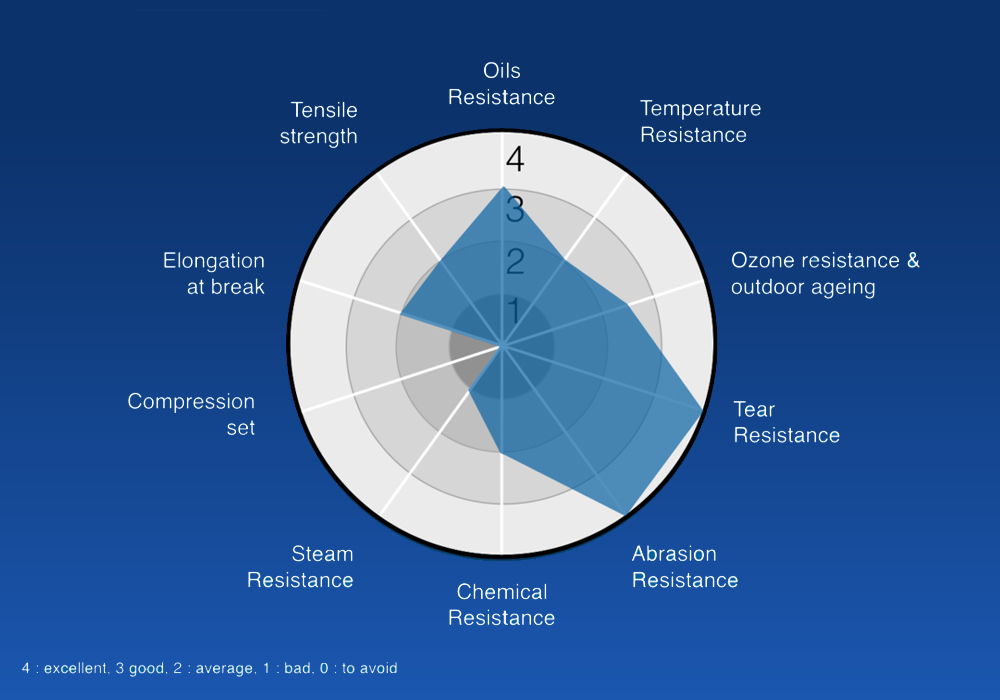
The properties of TPU in terms of abrasion resistance, colorability, high impact resistance, and flexibility at low temperatures can be enhanced. This combination also shows good resistance to fuels and oils, as well as high melt flow characteristics.
Special properties of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
- High elasticity
- Good compressive properties
- Double resistance
- Impact resistance
- Abrasion resistance
- Moisture resistance
- Hydrocarbon resistance
- Extremely high adhesion to various surfaces
- No dripping in vertical seams
- Retains flexibility over a very wide range
- Non-toxic and certified for use in proximity to drinking water
- High resistance to corrosive agents
- Lower cost and very lightweight
- Easy transportation and ability to pass through construction equipment
- Repairable and low water absorption
- No discoloration or cracking over time
- High and rapid lightfastness and colorability
- Quick and easy installation in the shortest possible time
- High insulation strength
- Low price for thermoplastic polyurethane granules
Capabilities of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
- Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) can be colored through various processes.
- Unlike other thermoplastic elastomers, TPU has special physical properties that place it among the most unique and widely used super-flexible materials.
- In the molding of products installed on vehicle bodies, it is combined with glass fibers or mineral fibers.
- In addition to properties such as abrasion resistance, colorability, high impact resistance, and good flexibility at low temperatures, TPU also possesses other characteristics such as good resistance to fuels and oils and suitable flow properties in the molten state.
Applications of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)

Decorative glass coatings, automotive body accessories, small wheels (wheelbarrows, hospital beds, etc.), tuning parts and CV joints for vehicles, automotive belts, films and sheets, fire hoses, flexible pipes, food production equipment, shoes and outsoles for sports shoes, hydraulic hoses, hydraulic seals, inflatable boats, skate wheels, magnetic tools, medical tubing and instruments, cord rollers used in mining, sports equipment, diving and swimming gear, TPU coating on fabric, protective cable and wire coverings, mobile phone protectors, computer keyboard protectors.
| Markets and Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Interior car parts such as gear knobs, instrument panels or console parts must meet stringent requirements in terms of surface quality, aging, abrasion and scratch resistance, while being cost-effective: TPU’s unique combination of scratch properties makes it an excellent choice for the automotive market. Its very fast cycling performance makes thermoplastic polyurethane a more cost-effective solution for molders. |
| Agriculture | The agricultural market demands strength and durability of the materials used. One application is animal identification tags used for livestock. Thermoplastic polyurethane offers excellent flexibility, weather and tear resistance in a wide range of climates. Special color and additive packages enable the design of flexible, laser-markable or smart (with microchip) ear tags. |
| TPU Films | TPU-based films offer outstanding performance for a wide range of end products. Among the most common application areas for thermoplastic polyurethane films are: textile coatings, apparel, adhesive and barrier films. Various processing techniques can be used to obtain free or multilayer films and sheets, including T-die and blown film extrusion and calendaring. |
| Seals and Gaskets | Specific TPU materials have been developed to meet the growing demand for high-performance polymeric materials with low compression set and excellent abrasion and oil resistance for seals: improved flow properties and high hydrolysis resistance of industrial high-pressure hydraulic seals. Low compression set at elevated temperatures. |
| Textile Coatings | TPUs are used in a wide range of textile coatings with end uses such as conveyor belts, inflatable items or military equipment. Compatible with calendaring processes. Excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, weldability and outdoor durability. |
| Sports and Leisure | Thanks to their unique combination of outstanding low-temperature flexibility, good impact and environmental resistance, as well as transparency, TPUs are the material of choice for many sports and leisure sectors. Excellent colorability transparency. |
| Belt and Profile Industry | TPUs are well established in the belts and profiles industry, where they are used to produce top-quality products such as timing belts, transmission belts or conveyor belt profiles. Low creep and exceptional mechanical strength in high extruded wall thicknesses and demonstrates outstanding weld strength. |
| Tubes and Hoses | Highly demanding applications, such as pneumatic tubes or hydraulic/wire bonding hoses, require tough and resistant materials with outstanding processing behavior in extrusion. TPUs offer excellent durability and abrasion properties for applications like hoses for solid material handling. In addition to chemical, mechanical and kink resistance, thermoplastic polyurethane brings flexibility across a wide range of temperatures. |
